- Autoimmune disease means when our body’s defense mechanisms mistakenly attacks and destroys a healthy body tissues : Celiac disease
Celiac disease is triggered by a response to gliadin, a prolamin (gluten protein) that discovered in wheat gluten, and same proteins contained in the plants of the tribe Triticeae (such as other common grains including barley and rye).
After being exposed to gliadin, and specifically to 3 peptides discovered in prolamin, the enzyme tissue transglutaminase changes the protein, and then the body's defense mechanisms cross-responds with the small-intestinal tract tissue which can causing an inflammatory response. Which leads to some truncating within the villi lining the small intestine. This is can disturbs with the ingestion of nutrients mainly because the intestinal villi are liable for absorption.
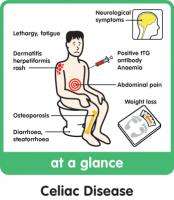
Signs and symptoms include painfulness and uncomfortableness in the gastrointestinal system, severe bowel obstruction and diarrhea, inability to develop (in small children), anemia and tiredness, but these might be absent, and signs and symptoms in some other body organ systems have been completely described. Vitamin deficiencies are often noted in people who suffered with celiac disease due to the minimized capability within the small intestine to absorb a nutrients.
A few tests that can be used to help in medical diagnosis. First, serological blood lab tests are usually the first-line examination needed to come up with a examination of celiac disease. Second, an superior endoscopy with biopsy within the duodenum or jejunum. Third, for the further more examinations might be carried out to determine additional complications, for example iron deficiency (by full blood count and iron studies), folic acid and vitamin B12 deficit and hypocalcaemia (low calcium levels, often because of vitamin D levels decreased).
Thyroid function tests could possibly be required during blood tests to determine hypothyroidism, which is prevalent in people who have celiac disease. Osteopenia and osteoporosis, mildly and seriously minimized bone mineral mass, are usually existing in people who have celiac disease, and examinations to determine bone mass might be performed for example dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scanning, to determine a possibility of bone fracture and require for bone protection prescribed medication.
The only known EFFECTIVE treatment is a life long gluten-free diet plan. No treatment is available that will reduce deterioration or avoid the human body from destroying the gut when gluten is found. Strict sticking with to the diet plan facilitates the intestines to heal. The diet plan could be complicated; inability to comply with the diet plan could potentially cause relapse.